Our Research
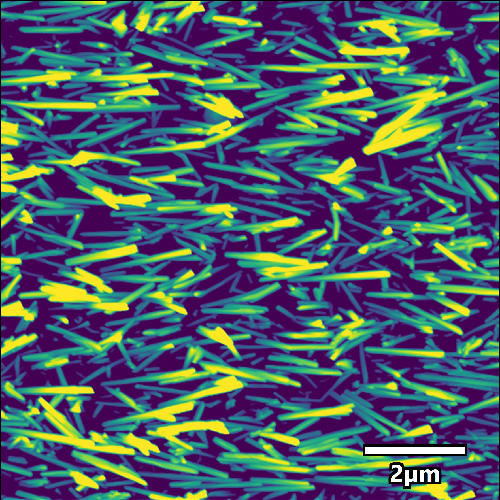
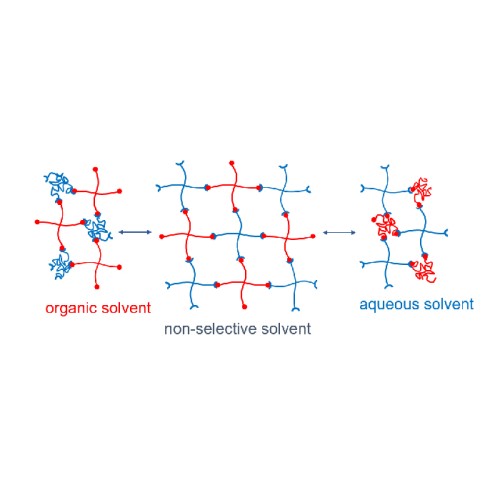
Such polymer brushes enable the coating of surfaces with organic thin films. Depending on the polymeric material, the properties of the polymer brush can be tailored for specific applications. This includes sensitivity to external stimuli, to which the PBes may respond (e.g. temperature, pH, …).
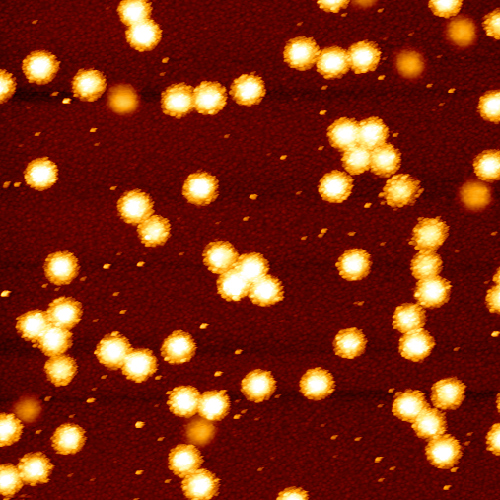
Furthermore, PBes can be used to immobilize small particles introducing additional properties to the so-called composite material. One of many existing examples is the attachment of inorganic nanoparticles (e.g. gold or cobalt nanoparticles) to the PBes.
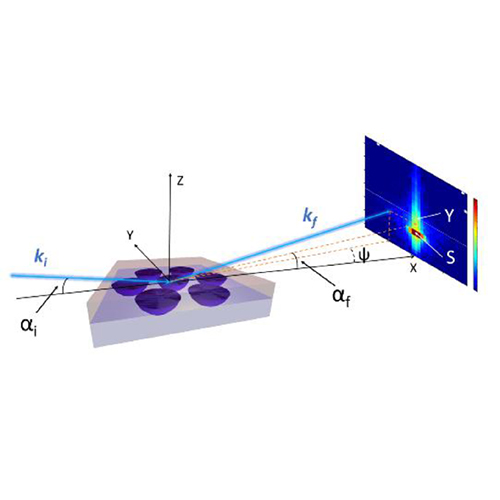
The group synthesizes PBs via Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (SI-ATRP) reaction. Frequently used analysis methods for the polymer brushes are ellipsometry, AFM, X-ray (XRR), and neutron reflectometry (NR).
Contacts:
Elias Hallenbach
Philipp Ritzert
Selected publications:
- Boyaciyan, Dikran; von Klitzing, R (2019): Stimuli-responsive polymer/metal composites: From fundamental research to self-regulating devices, Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 442019. pp. 193-207
- Boyaciyan, Dikran; Braun, Larissa; Löhmann, Oliver; Silvi, Luca; Schneck, Emanuel; von Klitzing, Regine (2018): Gold nanoparticle distribution in polyelectrolyte brushes loaded at different pH conditions, The Journal of Chemical Physics, 149 (16), p. 163322.
- Christau, Stephanie; Moeller, Tim; Genzer, Jan; Koehler, Ralf; von Klitzing, Regine (2017): Salt-Induced Aggregation of Negatively Charged Gold Nanoparticles Confined in a Polymer Brush Matrix, Macromolecules 2017, 50, 18, pp. 7333-7343